What Is Teething and When Does It Start?
The dentition (teething), which is called the appearance of the tooth in the mouth, starts on average in the 6th month and continues until the age of 2.5 years. Teeth in babies generally come out in accordance with the genetic order. The dentition age may be earlier or later, depending on the age of the parent's first tooth. Some babies may even be born with teeth.
What Are the Symptoms of Teething?
Teething symptoms and severity vary from baby to baby. While some babies get through this process lightly, in others this process is as toothy as its name and can force both the mother and the baby. In this case;
Increased saliva (saliva) production
Pain and restlessness
Redness and swelling of the gums
Redness in the cheek and chin area
Bite
Insomnia
Anorexia
Ear pulling, cheek scratching
What Can Mothers With Teething Baby Do?

Applying light pressure to the gingiva: the gingiva can be massaged with a clean and cold cloth.
Use of teether: You can give your baby teether that does not contain harmful plastic derivatives (bpa) and dyes, after keeping them in the refrigerator for a while, and you can make them scratch their gums. Care should be taken not to keep the scratcher in the freezer. Otherwise, it may stick to your baby's tongue, cheek and lip.
Giving cold foods: By giving cold fruit purees and water to your baby who has anorexia, you will both alleviate the pain and prevent the loss of nutrients and water.
Use of drugs to reduce pain: Syrups containing paracetamol or ibuprofen may be helpful in reducing pain. However, it is more appropriate not to use too much medication while teething, because it can reduce the fever caused by another underlying disease, leaving you and your dentist unaware of that disease.
Importance of Primary Teeth
In our country, Primary teeth are not given importance by most individuals because they are teeth that change when the time comes. However, due to the loss of Primary teeth in the early period, more serious problems are encountered in the future. For this reason, it is necessary to know the importance and duties of Primary teeth very well.
The primary task of Primary teeth is to ensure the proper nutrition of the child.
The proper development of speech also depends on the presence of Primary teeth.
Primary teeth protect the area they cover for the permanent tooth that will replace them and guide it while the permanent tooth is erupting.
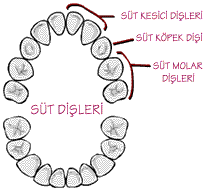
When the primary tooth is lost in the early period, this natural place-holding function also disappears.
The caries formed in the Primary teeth create foci of infection in the child, and also make feeding difficult. Loss of Primary teeth can negatively affect the appearance and speech of the child, and may pave the way for psychological problems in the child.
The caries formed in the Primary teeth create foci of infection in the child, and also make feeding difficult. Loss of Primary teeth can negatively affect the appearance and speech of the child, and may pave the way for psychological problems in the child.
Why Do Primary Teeth Rot Quickly?
Primary teeth contain more organic matter than normal teeth, so they are more prone to decay; they rot more easily and quickly.
Children cannot interpret signals such as hot-cold sensitivity and mild pain, which can be seen in the early period of caries, in a timely manner. They realize the event only when the pain is unbearable, in which case it may be too late.
Children cannot pay as much attention to oral care as adults. The child's dexterity, curiosity and parent's attitude determine the tooth brushing habit.
A common mistake, especially by mothers, is dipping a pacifier or bottle into foods such as candy, jam, etc., and giving them to children, or getting them accustomed to foods such as sugary Primary and fruit juice between naps. Thus, the teeth become susceptible to decay due to nutritional irregularities.
Should Caries in Primary Teeth Be Treated?
Considering the importance of Primary teeth and their duties in the mouth, if there is still time for the tooth under the Primary tooth to erupt, the caries in the Primary teeth should definitely be treated. Decayed and inflamed teeth that cannot be treated with teeth that have reached the age of replacement are extracted. However, if there is still time for the new permanent tooth to come out, a placeholder must be made to prevent the gap of the extracted tooth from closing.
Can Caries in Primary Teeth Be Prevented?
Dental caries usually starts in the grooves called "fissures" on the chewing surfaces of the molars and premolars. Caries can be prevented by covering the grooves with fissure sealants and preventing the infiltration of microbes, food residues, etc. into that area. This procedure can also be applied to permanent molars and premolars that erupt from the age of 6 years.
Another way to prevent caries is to increase the resistance of teeth to caries. With the application of superficial fluoride to the teeth, the resistance of the teeth is increased.
Another way to prevent caries is to increase the resistance of teeth to caries. With the application of superficial fluoride to the teeth, the resistance of the teeth is increased.



 Turkish
Turkish Deutsch
Deutsch